Calendar 2025: A Comparative Analysis of the Hijri and Gregorian Calendars
Related Articles: Calendar 2025: A Comparative Analysis of the Hijri and Gregorian Calendars
- Bi-Weekly Payroll Calendar 2025
- 2025 Calendar UK Excel: A Comprehensive Guide To Creating And Customizing Calendars
- Sunday, January 1, 2025: A Pivotal Day In The Jewish Calendar
- OC Calendar 2025 Printable Excel: A Comprehensive Guide To Planning And Organization
- Excel Calendar Template For January 2025
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Calendar 2025: A Comparative Analysis of the Hijri and Gregorian Calendars. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Video about Calendar 2025: A Comparative Analysis of the Hijri and Gregorian Calendars
Calendar 2025: A Comparative Analysis of the Hijri and Gregorian Calendars
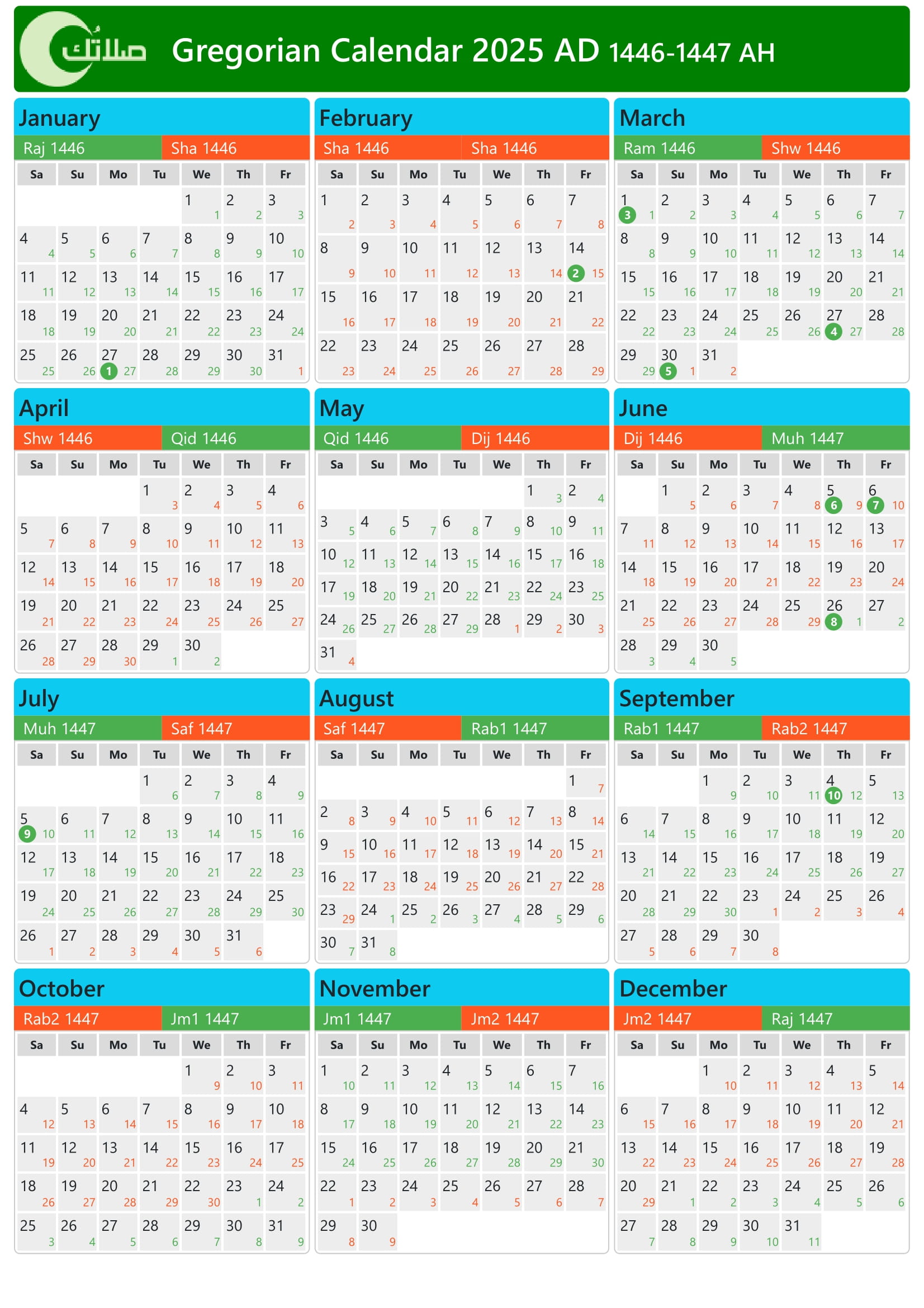
Calendars serve as essential tools for organizing and tracking time, providing a framework for human activities and societal functions. Two widely used calendars are the Hijri and Gregorian calendars, each rooted in distinct cultural and religious traditions. This article presents a comprehensive comparison of the Hijri and Gregorian calendars for the year 2025, examining their origins, structure, and key differences.
Origins and History
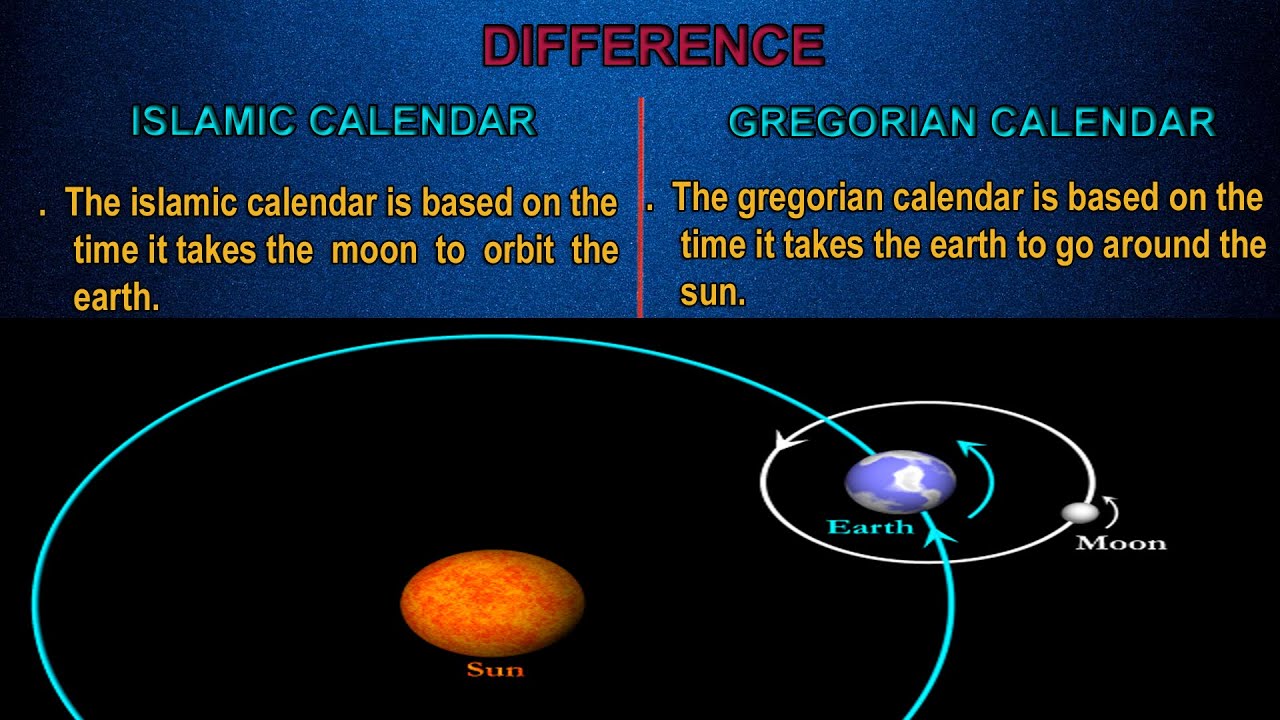
The Hijri calendar, also known as the Islamic calendar, is a lunar calendar that originated in the 7th century CE during the time of the Prophet Muhammad. The calendar’s starting point is the Hijra, Muhammad’s migration from Mecca to Medina in 622 CE. The Hijri calendar consists of 12 lunar months, with each month beginning with the sighting of the new moon.
The Gregorian calendar, named after Pope Gregory XIII, is a solar calendar that was introduced in 1582 CE as a reform of the Julian calendar. The Gregorian calendar is based on the Earth’s orbit around the sun and consists of 12 months with varying lengths.
Structure and Duration
The Hijri calendar is a lunar calendar, meaning that it is based on the phases of the moon. A lunar month is approximately 29.5 days long, resulting in a year of approximately 354 days. The Hijri year is shorter than the Gregorian year by about 11 days.
The Gregorian calendar, on the other hand, is a solar calendar, meaning that it is based on the Earth’s orbit around the sun. A solar year is approximately 365.25 days long, resulting in a year of 365 days in most years and 366 days in leap years.
Months and Days
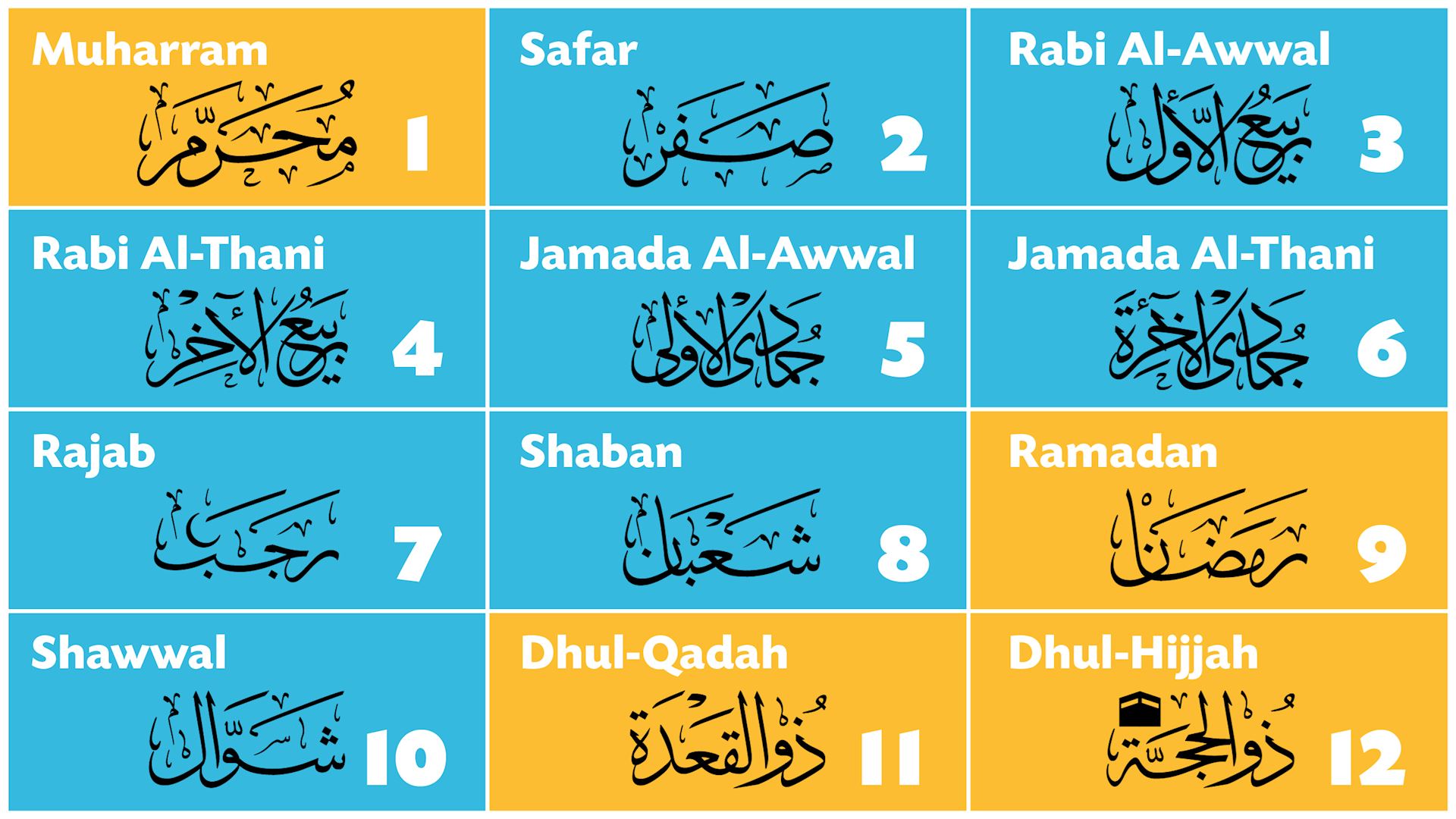
The Hijri calendar consists of 12 lunar months, each with 29 or 30 days. The months are named after Arabic words related to their seasons or significant events. The first month of the Hijri year is Muharram, followed by Safar, Rabi’ al-Awwal, Rabi’ al-Thani, Jumada al-Ula, Jumada al-Thaniyya, Rajab, Sha’ban, Ramadan, Shawwal, Dhu al-Qi’dah, and Dhu al-Hijjah.
The Gregorian calendar also consists of 12 months, but their lengths vary. The months are named after Roman deities or numbers. The first month of the Gregorian year is January, followed by February, March, April, May, June, July, August, September, October, November, and December.
Leap Years
In the Hijri calendar, there is no concept of leap years. The length of the year is fixed at 354 days. This means that the Hijri calendar gradually shifts relative to the solar year, completing a full cycle approximately every 33 years.
In the Gregorian calendar, leap years occur every four years, except for years that are divisible by 100 but not by 400. In leap years, an extra day is added to the month of February, resulting in a year of 366 days.
Religious Significance
The Hijri calendar holds significant religious importance in Islam. The month of Ramadan, the ninth month of the Hijri year, is a time of fasting and spiritual reflection for Muslims. Other important Islamic holidays, such as Eid al-Fitr and Eid al-Adha, are also determined by the Hijri calendar.
The Gregorian calendar has no direct religious significance, but it is widely used in Christian countries and has become the de facto international calendar for civil and business purposes.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Hijri Calendar | Gregorian Calendar |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Lunar | Solar |
| Starting Point | Hijra (622 CE) | Gregorian Reform (1582 CE) |
| Year Length | Approximately 354 days | 365 days (366 in leap years) |
| Months | 12 lunar months | 12 months with varying lengths |
| Leap Years | None | Every four years (except years divisible by 100 but not by 400) |
| Religious Significance | Important in Islam | No direct religious significance |
Implications for Daily Life
The different structures and durations of the Hijri and Gregorian calendars have implications for daily life in different cultures and regions. For example, in Muslim-majority countries, the Hijri calendar is used to determine religious holidays and observances. In contrast, the Gregorian calendar is used in most Western countries for civil and business purposes, including scheduling appointments, setting deadlines, and planning events.
Conclusion
The Hijri and Gregorian calendars are two distinct and widely used calendars that have played significant roles in human history and societal organization. The Hijri calendar, rooted in Islamic traditions, is a lunar calendar that is particularly important in Muslim communities. The Gregorian calendar, based on the solar year, is the de facto international calendar for civil and business purposes. Understanding the differences and similarities between these two calendars is essential for navigating the complexities of timekeeping in a globalized world.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Calendar 2025: A Comparative Analysis of the Hijri and Gregorian Calendars. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
